Acwing 🔗
二分 🔗
最佳牛围栏 🔗
农夫约翰的农场由 N 块田地组成,每块地里都有一定数量的牛,其数量不会少于 1 头,也不会超过 2000 头。
约翰希望用围栏将一部分连续的田地围起来,并使得围起来的区域内每块地包含的牛的数量的平均值达到最大。
围起区域内至少需要包含 F 块地,其中 F 会在输入中给出。
在给定条件下,计算围起区域内每块地包含的牛的数量的平均值可能的最大值是多少。
输入格式 🔗
第一行输入整数 N 和 F,数据间用空格隔开。
接下来 N 行,每行输入一个整数,第 i+1 行输入的整数代表第 i 片区域内包含的牛的数目。
输出格式 🔗
输出一个整数,表示平均值的最大值乘以 1000 再 向下取整 之后得到的结果。
数据范围 🔗
1≤N≤100000 1≤F≤N
输入样例: 🔗
10 6
6
4
2
10
3
8
5
9
4
1
输出样例: 🔗
6500
解析 🔗
可能的最大值,关键字,考虑二分,假设存在某一个平均值满足题目条件,那么小于该值的平均值一定也满足题目条件,而大于该值的平均值不一定满足条件,符合二分的性质。
为了快速判断某一区间的值是否大于我们二分的平均值,我们可以让每个数减去平均值,再求前缀和,只要判断是否存在非负的和即可(同时要保证长度大于等于F)
代码 🔗
package Young.AcWing.binary;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @fileName: cows
* @author: 小杨的华为
* @date: 2022/12/4 11:32
* @email: 1683209437@qq.com
*/
public class cows {
static final int N = 100010;
static int n,f;
static int[] a = new int[N];
static double[] s = new double[N];
static boolean check(double avg){
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i] - avg; //求前缀和
}
double minv = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = f; j <= n; i++, j++){
minv = Math.min(minv,s[i]);
if(s[j] >= minv)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
f = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
double l = 0, r = 2000;
while (r - l > 0.00001){
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(check(mid))
l = mid;
else
r = mid;
}
System.out.println((int)(r*1000));
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// typedef long long ll;
const int N = 100010;
int n,f;
int a[N];
double s[N];
int res;
bool check(double avg){
s[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i] - avg; //求出前缀和
}
double minv = 0;
for(int i = 0, j = f; j <= n; i++, j++){
minv = min(minv,s[i]);
if(s[j] >= minv)
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&f);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
double l = 1, r = 2000; //平均值最小为1,最大为2000
while(r - l > 1e-5){
double mid = (l+r) / 2;
if(check(mid))
l = mid;
else
r = mid;
}
printf("%d\n",(int)(r*1000));
return 0;
}
差分 🔗
增减序列 🔗
给定一个长度为 nn 的数列 a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an,每次可以选择一个区间 [l,r][l,r],使下标在这个区间内的数都加一或者都减一。
求至少需要多少次操作才能使数列中的所有数都一样,并求出在保证最少次数的前提下,最终得到的数列可能有多少种。
输入格式 🔗
第一行输入正整数 nn。
接下来 nn 行,每行输入一个整数,第 i+1i+1 行的整数代表 aiai。
输出格式 🔗
第一行输出最少操作次数。
第二行输出最终能得到多少种结果。
数据范围 🔗
0<n≤1050<n≤105, 0≤ai<21474836480≤ai<2147483648
输入样例: 🔗
4
1
1
2
2
输出样例: 🔗
1
2
解析 🔗
对数组一段区间进行加或者减:
差分最后要得到的差分数组除了第一个数,其它全是0,由于差分数组中可能有整数/负数,基于差分的性质,我们可以使这样的一对数,使正数减1,负数加1(对应于在原数组中的这段区间内进行了一次加/减1操作),之后差分数组只剩下同符号的数,剩下的同符号的数只能通过b[1]或者b[i+1]两个对差分数组没有影响的来一个一个的把自己减为0。
所以操作次数最小为:min(pos,neg) + abs(pos - neg); //参数含义见代码
种类数量最少为:abs(pos - neg) + 1;
代码 🔗
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static final int N = 100010;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// String[] s = br.readLine().split(" ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[N];
int[] b = new int[N]; //差分数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n ; i++) {
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
b[i] = a[i] - a[i-1];
}
long pos = 0, neg = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if(b[i] > 0)
pos += b[i]; //正数的和
else
neg -= b[i]; //负数的和的绝对值
}
System.out.println(Math.min(pos,neg) + Math.abs(pos - neg));
System.out.println(Math.abs(pos - neg) + 1);
}
}
单调栈 🔗
直方图中最大的矩形 🔗
直方图是由在公共基线处对齐的一系列矩形组成的多边形。
矩形具有相等的宽度,但可以具有不同的高度。
例如,图例左侧显示了由高度为 2,1,4,5,1,3,32,1,4,5,1,3,3 的矩形组成的直方图,矩形的宽度都为 11:
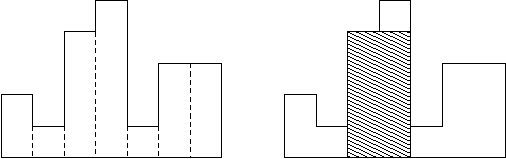
通常,直方图用于表示离散分布,例如,文本中字符的频率。
现在,请你计算在公共基线处对齐的直方图中最大矩形的面积。
图例右图显示了所描绘直方图的最大对齐矩形。
输入格式 🔗
输入包含几个测试用例。
每个测试用例占据一行,用以描述一个直方图,并以整数 nn 开始,表示组成直方图的矩形数目。
然后跟随 nn 个整数 h1,…,hnh1,…,hn。
这些数字以从左到右的顺序表示直方图的各个矩形的高度。
每个矩形的宽度为 11。
同行数字用空格隔开。
当输入用例为 n=0n=0 时,结束输入,且该用例不用考虑。
输出格式 🔗
对于每一个测试用例,输出一个整数,代表指定直方图中最大矩形的区域面积。
每个数据占一行。
请注意,此矩形必须在公共基线处对齐。
数据范围 🔗
1≤n≤1000001≤n≤100000, 0≤hi≤10000000000≤hi≤1000000000
输入样例: 🔗
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0
输出样例: 🔗
8
4000
解析 🔗
首先考虑如何用最朴素的想法做出本题,我们可以枚举每一个矩形作为右边界,再枚举每个左边界,取最大值,时间复杂度为O(n^2),现在考虑如何优化,可以知道答案中的矩形高度一定是图中的某个矩形的高度,我们可以枚举每一个矩形的高度,让它向两边扩展,当遇到不比它矮的就继续扩展,遇到比它矮的就停止扩展,这样问题就转化为了寻找某个矩形左边/后边第一个比它矮的矩形,正是单调栈的性质,O(n)。
代码 🔗
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
static final int N = 100010;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n;
while (scanner.hasNext()){
n = scanner.nextInt();
if(n == 0)
break;
long res = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int[] h = new int[N];
int[] l = new int[N];
int[] r = new int[N];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
h[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
h[0] = -1; //设置两个边界
h[n+1] = -1;
stack.push(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
while (h[i] <= h[stack.peek()]){
stack.pop();
}
l[i] = stack.peek();
stack.push(i);
}
stack.clear();
stack.push(n+1);
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
while (h[i] <= h[stack.peek()]) {
stack.pop();
}
r[i] = stack.peek();
stack.push(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
res = Math.max(res, (long) h[i] * (r[i] - l[i] - 1));
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
堆 🔗
序列 🔗
给定 m 个序列,每个包含 n 个非负整数。
现在我们可以从每个序列中选择一个数字以形成具有 m 个整数的序列。
很明显,我们一共可以得到 n^m个这种序列,然后我们可以计算每个序列中的数字之和,并得到 n^m 个值。
现在请你求出这些序列和之中最小的 n 个值。
输入格式 🔗
第一行输入一个整数 T,代表输入中包含测试用例的数量。
接下来输入 T 组测试用例。
对于每组测试用例,第一行输入两个整数 m 和 n。
接下在 m 行输入 m 个整数序列,数列中的整数均不超过 10000。
输出格式 🔗
对于每组测试用例,均以递增顺序输出最小的 n 个序列和,数值之间用空格隔开。
每组输出占一行。
数据范围 🔗
0<m≤1000, 0<n≤2000
输入样例: 🔗
1
2 3
1 2 3
2 2 3
输出样例: 🔗
3 3 4
解析 🔗
首先是维护顺序问题,需要用到堆
其次是多组,分组思想
以两组数据为例,合并为一组有序之后再与第三组合并,以此类推,进行m-1次合并,即可得到答案。
两组数据如何维护和的最小值,可以通过两个指针分别指向两个有序数组,每次选取其中一个进行后移,在这需要考虑去重问题。
但代码中的思想比较巧妙,不需要去重,值得深思。
代码 🔗
/*
* Filename: d:\SHU\Acwing\cpp\heap\sequence.cpp
* Path: d:\SHU\Acwing\cpp\heap
* Created Date: Saturday, December 17th 2022, 12:36:01 pm
* Author: Young
*
* Copyright (c) 2022 Your Company
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e3+10;
int n,m;
int a[N],b[N],c[N];
void merge(){
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>> heap; //小顶堆
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
heap.push({a[0] + b[i],0});
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int s = t.first, p = t.second;
c[i] = s;
heap.push({s - a[p] + a[p+1],p+1});
}
memcpy(a,c,4*n);
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while (t--){
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a,a+n);
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> b[j];
}
merge();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @fileName: sequence
* @author: Young
* @date: 2022/12/17 9:34
* @email: 1683209437@qq.com
*/
public class Main {
static final int N = 2010;
static final int M = 1010;
static int[] a,b,c;
static {
a = new int[N];
b = new int[N];
c = new int[N];
}
static class Node {
int x;
int y;
boolean ok;
Node(int x, int y, boolean ok) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.ok = ok;
}
Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static void merge(int n){
PriorityQueue<Node> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(((o1, o2) -> o1.x - o2.x)); //小顶堆
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
heap.add(new Node(a[1]+b[i],1));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Node node = heap.poll();
assert node != null;
int s = node.x, p = node.y;
c[i] = s;
heap.add(new Node(s - a[p] + a[p+1], p+1));
}
System.arraycopy(c,1,a,1,n);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n,m,t;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
t = scanner.nextInt();
while ((t--) != 0) {
m = scanner.nextInt();
n = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(a,1,n + 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
b[j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
merge(n);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
数据备份 🔗
你在一家 IT 公司为大型写字楼或办公楼的计算机数据做备份。
然而数据备份的工作是枯燥乏味的,因此你想设计一个系统让不同的办公楼彼此之间互相备份,而你则坐在家中尽享计算机游戏的乐趣。
已知办公楼都位于同一条街上,你决定给这些办公楼配对(两个一组)。
每一对办公楼可以通过在这两个建筑物之间铺设网络电缆使得它们可以互相备份。
然而,网络电缆的费用很高。
当地电信公司仅能为你提供 K 条网络电缆,这意味着你仅能为 K 对办公楼(总计 2K 个办公楼)安排备份。
任意一个办公楼都属于唯一的配对组(换句话说,这 2K 个办公楼一定是相异的)。
此外,电信公司需按网络电缆的长度(公里数)收费。
因而,你需要选择这 K 对办公楼使得电缆的总长度尽可能短。
换句话说,你需要选择这 K 对办公楼,使得每一对办公楼之间的距离之和(总距离)尽可能小。
下面给出一个示例,假定你有 5 个客户,其办公楼都在一条街上,如下图所示。
这 5 个办公楼分别位于距离大街起点 1km,3km,4km,6km 和 12km 处。
电信公司仅为你提供 K=2 条电缆。
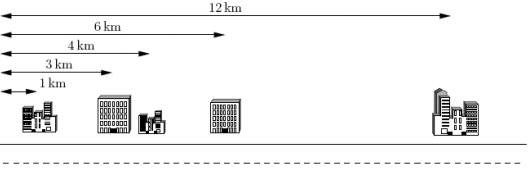
上例中最好的配对方案是将第 1 个和第 2 个办公楼相连,第 3 个和第 4 个办公楼相连。
这样可按要求使用 K=2 条电缆。
第 1 条电缆的长度是 3km−1km=2km,第 2 条电缆的长度是 6km−4km=2km。
这种配对方案需要总长 4km 的网络电缆,满足距离之和最小的要求。
输入格式 🔗
第一行输入整数 n 和 K,其中 n 表示办公楼的数目,K 表示可利用的网络电缆的数目。
接下来的 n 行每行仅包含一个整数 s,表示每个办公楼到大街起点处的距离。
这些整数将按照从小到大的顺序依次出现。
输出格式 🔗
输出应由一个正整数组成,给出将 2K 个相异的办公楼连成 K 对所需的网络电缆的最小总长度。
数据范围 🔗
2≤n≤100000, 1≤K≤n/2, 0≤s≤10000000000
输入样例: 🔗
5 2
1
3
4
6
12
输出样例: 🔗
4
解析 🔗
优先队列 + 双向链表
数学归纳法,找出其中的规律,有种容斥的思想
加入双向链表实现后悔
代码 🔗
*****
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static final int N = 100010;
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> { //相邻的建筑物之间的距离抽象为一个节点
Node pre;
Node next;
Long val;
Node(Long val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return val <= o.val ? -1 : 1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n, k;
n = scanner.nextInt();
k = scanner.nextInt();
PriorityQueue<Node> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
Node pre = null;
long preIndex = scanner.nextLong();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
long curIndex = scanner.nextLong();
Node curNode = new Node(curIndex - preIndex);
preIndex = curIndex;
heap.offer(curNode);
if (pre == null) {
pre = curNode;
} else {
curNode.pre = pre;
pre.next = curNode;
pre = curNode;
}
}
long res = 0;
while ((k--) != 0) {
Node cur = heap.poll();
assert cur != null;
res += cur.val;
if (k == 0)
continue;
Node preNode = cur.pre;
Node nextNode = cur.next;
if (preNode == null) {
cur.next.next.pre = null;
heap.remove(nextNode);
} else if (nextNode == null) {
cur.pre.pre.next = null;
heap.remove(preNode);
} else {
long insertVal = preNode.val + nextNode.val - cur.val;
Node node = new Node(insertVal);
if (preNode.pre != null) {
preNode.pre.next = node;
node.pre = preNode;
}
if (nextNode.next != null) {
nextNode.next.pre = node;
node.next = nextNode;
}
heap.remove(preNode);
heap.remove(nextNode);
heap.offer(node);
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
最短路 🔗
Prim 🔗
雨 🔗
海里有一个小岛。
岛可以描述为一个具有 R 行 C�列的矩阵,其中包含的数字 H [i] [j]表示每个单元格的高度。
以下是一个 3×3 岛屿的示例:
3 5 5
5 4 5
5 5 5
有时,大雨会在这个岛上的每个单元格上均匀地降落。
你可以假设降水量可以是无限大。
在这样的大雨之后,岛上的一些区域(由沿着边缘连接的一个或多个单元格形成)可能会存在积水。
一片区域可以存在积水的前提是与该区域内单元格沿着边缘连接的区域外的单元格的高度均高于区域内单元格。(周围的海洋被视为高度为 00 的无限单元格。)
否则,水将始终流入其他区域并最终出海。
你可以假设海的高度永远不会改变。
在大雨过后,我们将使用 W[i] [j]来表示岛屿上每个单元格的高度。
以下是对大雨过后的示例岛屿的高度的分析。
最中央的初始高度为 4 的单元格被初始高度为 5 的单元格包围着,因此在该单元格将产生积水,在积水高度到达 5 以后,没有更多区域被高度更高的单元格包围,因此将不再继续积水。
请注意,水不会直接在两个共享顶点的单元格之间流动;水必须沿着共同的边缘流动。(所以中央单元格的积水不会从左上角处流走)
以下是雨后示例岛屿的高度:
3 5 5
5 5 5
5 5 5
给定岛的高度矩阵,你能计算出大雨后的每个单元格的增加高度(W[i] [j]−H[i] [j])的总和吗?
输入格式 🔗
第一行包含整数 T,表示共有 T组测试数据。
每组数据第一行包含两个整数 R和 C。
接下来 R行每行包含 C个整数 H[i] [j],表示矩阵内单元格的高度。
输出格式 🔗
每组数据输出一个结果,每个结果占一行。
结果表示为 Case #x: y,其中 x 是组别编号(从 1 开始),y是增加高度的总和。
数据范围 🔗
1≤T≤100, 1≤H[i] [j]≤1000, 1≤R,C≤50
输入样例: 🔗
3
3 3
3 5 5
5 4 5
5 5 5
4 4
5 5 5 1
5 1 1 5
5 1 5 5
5 2 5 8
4 3
2 2 2
2 1 2
2 1 2
2 1 2
输出样例: 🔗
Case #1: 1
Case #2: 3
Case #3: 0
样例解释 🔗
样例#1已经在题目中说明。
在样例#2中,雨后岛屿看起来像这样:
5 5 5 1
5 2 2 5
5 2 5 5
5 2 5 8
样例#3在雨后保持不变。
解析 🔗
边界上的点与海相邻,不可能产生积水,即边界点的最终状态和初始状态一致,矩阵中的每个点流向的方向只有上下左右,四向。
每个点产生的积水,取决于每个点到海的路径中的最大值的最小值(木桶效应)
由于边界的点的状态不会改变,初始时直接加入优先队列中,依次取出队头,向四个方向扩展,更新积水,并加入新的点(若该点可以积水,则加入积水后的该点)。
代码 🔗
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int R,C,T,seq = 0;
static int[][] H;
static boolean[][] vis;
static int ans;
static int[] dx = {0,0,-1,1};
static int[] dy = {-1,1,0,0};
static int prim() {
ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i)
Arrays.fill(vis[i],false);
PriorityQueue<Node> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->a.w - b.w);
for (int i = 1; i < R - 1; ++i) {
vis[i][0] = vis[i][C-1] = true;
heap.offer(new Node(i,0,H[i][0]));
heap.offer(new Node(i,C-1,H[i][C-1]));
}
for (int i = 1; i < C - 1; ++i) {
vis[0][i] = vis[R - 1][i] = true;
heap.offer(new Node(0,i,H[0][i]));
heap.offer(new Node(R - 1,i,H[R-1][i]));
}
vis[0][0] = vis[0][C-1] = vis[R-1][0] = vis[R-1][C-1] = true;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = heap.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nx = cur.x + dx[i], ny = cur.y + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= R || ny < 0 || ny >= C ||vis[nx][ny])
continue;
vis[nx][ny] = true;
ans += Math.max(0, cur.w - H[nx][ny]);
heap.offer(new Node(nx,ny,Math.max(cur.w,H[nx][ny])));
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
T = sc.nextInt();
while ((T--) > 0) {
seq++;
R = sc.nextInt();
C = sc.nextInt();
H = new int[R][C];
vis = new boolean[R][C];
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) {
H[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int x = prim();
System.out.println("Case #" + seq + ": " + x);
}
}
static class Node{
int x,y,w;
public Node(int x, int y, int w) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.w = w;
}
}
}
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int R = 55;
const int C = 55;
int r,c,t;
int H[R][C];
bool st[R][C];
int seq = 0,ans;
int dir[4][2] = {
{0,-1},
{0,1},
{-1,0},
{1,0}
};
struct Node {
int x,y,w;
bool operator< (const Node& node) const {
return w > node.w;
}
};
int prim() {
ans = 0;
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
priority_queue<Node> heap;
for (int i = 1; i < c - 1; ++i) {
st[0][i] = st[r-1][i] = true;
heap.push(Node{0,i,H[0][i]});
heap.push(Node{r-1,i,H[r-1][i]});
}
for (int i = 1; i < r - 1; ++i) {
st[i][0] = st[i][c-1] = true;
heap.push(Node{i,0,H[i][0]});
heap.push(Node{i,c-1,H[i][c-1]});
}
st[0][0] = st[0][c-1] = st[r-1][0] = st[r-1][c-1] = true;
while (!heap.empty()) {
auto cur = heap.top();
heap.pop();
st[cur.x][cur.y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nx = dir[i][0] + cur.x, ny = dir[i][1] + cur.y;
if (nx < 0 || nx >= r || ny < 0 || ny >= c || st[nx][ny])
continue;
ans += max(0, cur.w - H[nx][ny]);
heap.push(Node{nx,ny,max(cur.w,H[nx][ny])});
st[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
seq++;
cin >> r >> c;
for (int i = 0; i < r; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < c; ++j) {
cin >> H[i][j];
}
}
int x = prim();
cout << "Case #" << seq << ": " << x << endl;
}
return 0;
}
动态规划 🔗
线性DP 🔗
最长公共上升子序列 🔗
熊大妈的奶牛在小沐沐的熏陶下开始研究信息题目。
小沐沐先让奶牛研究了最长上升子序列,再让他们研究了最长公共子序列,现在又让他们研究最长公共上升子序列了。
小沐沐说,对于两个数列 A 和 B,如果它们都包含一段位置不一定连续的数,且数值是严格递增的,那么称这一段数是两个数列的公共上升子序列,而所有的公共上升子序列中最长的就是最长公共上升子序列了。
奶牛半懂不懂,小沐沐要你来告诉奶牛什么是最长公共上升子序列。
不过,只要告诉奶牛它的长度就可以了。
数列 A 和 B的长度均不超过 3000。
输入格式 🔗
第一行包含一个整数 N,表示数列 A,B的长度。
第二行包含 N 个整数,表示数列 A。
第三行包含 N 个整数,表示数列 B。
输出格式 🔗
输出一个整数,表示最长公共上升子序列的长度。
数据范围 🔗
1≤N≤3000,序列中的数字均不超过 2^31−1。
输入样例: 🔗
4
2 2 1 3
2 1 2 3
输出样例: 🔗
2
解析 🔗
本题结合了最长上升子序列和最长公共子序列的思想,dp状态定义为a[1-i]和b[1-j]中以b[j]结尾的公共上升子序列的集合,属性定义为Max,dp状态计算可以通过是否包含a[i]来划分,不包含则dp[i] [j] = dp[i-1] [j],包含则需要考虑该序列的倒数第二个数,可能为b[1 - j-1],我们需要通过枚举来求出符合条件的Max,此时需要三重循环,我们发现j是从小到大枚举的,我们可以通过在第二重循环维护一个maxV变量,即可直接得出dp[i] [j]。
代码 🔗
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static final int N = 3010;
static int n;
static int[] a;
static int[] b;
static int[][] dp;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
a = new int[n+1];
b = new int[n+1];
dp = new int[n+1][n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int maxV = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
if (a[i] == b[j])
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], maxV);
if (a[i] > b[j])
maxV = Math.max(maxV, dp[i-1][j] + 1);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[n][i]);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3010;
int n;
int dp[N][N];
int a[N],b[N];
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> b[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
int maxV = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
if (a[i] == b[j])
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], maxV);
if (a[i] > b[j])
maxV = max(maxV, dp[i-1][j] + 1);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
ans = max(ans, dp[n][i]);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}